Differences Between Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) and Business Intelligence (BI)

In the realm of corporate strategy and data analytics, two terms frequently arise: Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) and Business Intelligence (BI). While both are crucial for informed decision-making and organizational success, they serve distinct purposes and functions. Here, we explore the key differences between EPM and BI to help businesses understand how to leverage each effectively.
What is Enterprise Performance Management (EPM)?
Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) is a suite of processes, methodologies, metrics, and systems used by organizations to plan, monitor, and manage business performance. EPM integrates strategic planning, budgeting, forecasting, and financial reporting, aligning organizational objectives with performance metrics. Key components of EPM include:
Strategic Planning: Setting long-term goals and defining the strategies to achieve them.
Budgeting and Forecasting: Allocating resources and predicting future financial performance.
Financial Reporting: Generating reports to provide insights into financial health and performance.
Performance Analysis: Monitoring key performance indicators (KPIs) to track progress toward strategic goals.
EPM tools often include capabilities for financial consolidation, scenario modeling, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that organizations can respond swiftly to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
EPM tools often include capabilities for financial consolidation, scenario modeling, and regulatory compliance, ensuring that organizations can respond swiftly to changing market conditions and regulatory requirements.
What is Business Intelligence (BI)?
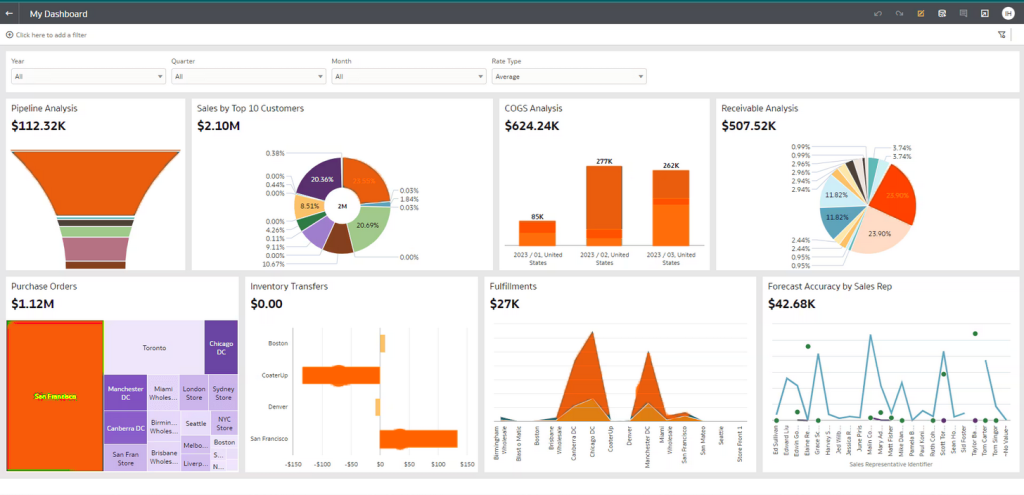
Business Intelligence (BI) encompasses the technologies, applications, and practices used to collect, integrate, analyze, and present business information. The primary goal of BI is to support better business decision-making by providing stakeholders with timely, accurate, and actionable data. Key components of BI include:
Data Warehousing: Storing large volumes of structured and unstructured data from various sources.
Data Mining: Analyzing data to discover patterns and relationships.
Reporting: Creating dashboards and reports to visualize data insights.
Analytics: Applying statistical and quantitative analysis to interpret data.
BI tools enable organizations to transform raw data into meaningful insights, facilitating data-driven decisions across all levels of the organization.
Key Differences Between EPM and BI
Focus and Objectives:
EPM: Concentrates on aligning business activities with strategic goals, ensuring optimal resource allocation, and improving overall performance. It is strategy-centric.
BI: Focuses on data analysis and reporting to support operational decision-making. It is data-centric.
Scope of Use:
EPM: Primarily used by executives and finance teams for high-level strategic planning and financial management.
BI: Used across various departments, including marketing, sales, operations, and finance, for day-to-day decision-making.
Tools and Technologies:
EPM: Utilizes tools like NetSuite EPM, Oracle EPM, SAP EPM, CCH Tagetik, Anaplan or IBM Cognos TM1, which are designed for financial consolidation, budgeting, and performance management.
BI: Employs tools such as NetSuite Analytics Datawarehouse, Oracle Analytics Cloud, Tableau, Power BI, and QlikView, which are geared toward data visualization, reporting, and dashboard creation.
Outcome and Benefits:
EPM: Aims to enhance strategic alignment, improve financial planning accuracy, and ensure compliance.
BI: Aims to provide comprehensive insights into business operations, identify trends, and drive operational efficiency.
Conclusion
While both Enterprise Performance Management (EPM) and Business Intelligence (BI) are integral to modern business operations, understanding their differences is crucial for effective implementation. EPM focuses on strategic planning and performance management, whereas BI emphasizes data analysis and operational insights.
By leveraging both NetSuite EPM and NetSuite Analytics Datawarehouse, NetSuite ERP users can achieve a balanced approach to strategy and operations, ensuring sustained growth and competitive advantage.
Learn more
Download the free whitepaper NetSuite Guide for Financial Projections (LinkedIn)
Visit our YouTube channel.
Follow us at LinkedIn
Comment at the LinkedIn article “Differences between EPM and BI”.